Plastic tubes are hollow channels that vary in length, diameter, wall thickness, and strength. Manufacturers and customers choose to work with plastic tubing products, rather than metal or rubber tubing, because it can be flexible and because it offers a much greater variety in material choice. Read More…
A leading manufacturer and fabricator of flexible plastic tubing and hose, we produce and stock large quantities of a wide variety of materials, including PVC, polyurethane, silicone, nylon and many more.
At Absolute Custom Extrusions, we specialize in plastic tubing, while providing custom plastic extrusions and profiles. Products include distributor tubes, hot or cold water tubes, automotive tubing, medical tubing, shipping tubes and golf club tubes.
Petro specializes in plastic tubing, offering custom extruded tubing, coiling & angle cutting. Our clear & color plastic tubing is available in Polycarbonate, Acrylic & PE-PP-Nylon.
We are a leading custom extruder of plastic shrink tubing, flexible as well as rigid tubing and profiles. Pexco offers tubing in a wide range of standard and custom colors in a multitude of material options like Polysulfone, PVC, polyurethane, nylon and more. We use state-of-the-art machinery and perform secondary operations on site, such as drilling, slotting, notching, etc. Pexco is ISO 9001...
GSH is a manufacturer of plastic, extruded, nylon, polycarbonate and polyethylene tubing. We serve a variety of industries with our products, including automotive, consumer, electrical and marine.
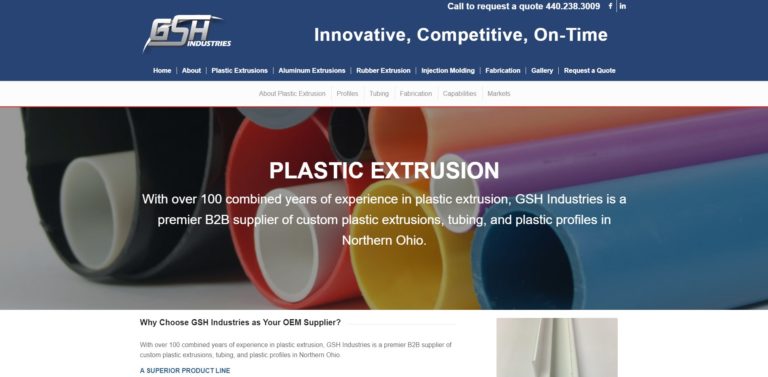
When you choose Plastic Extrusion Technologies, you can rest assured that your custom plastic tubing requirements will be met with precision and excellence. We take pride in being a leader in the custom plastic extrusion industry, consistently striving to exceed your expectations and deliver the solutions you need.
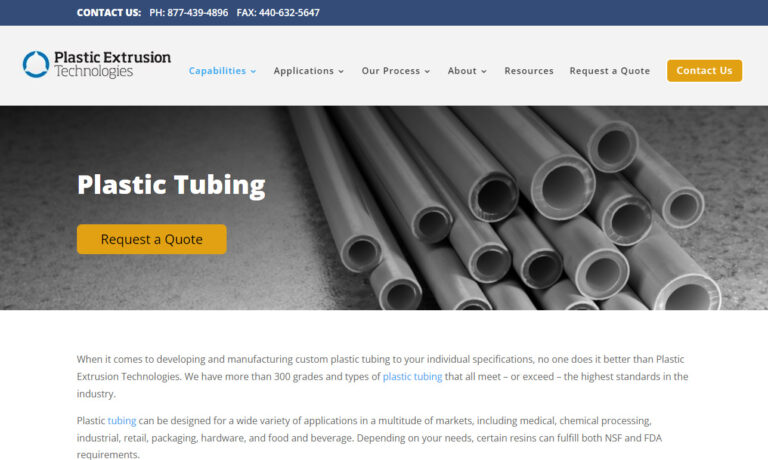
If you are in search of quality plastic tubing then you have found the company that can meet your needs. We have a wide variety of stock plastic tubing items and our solutions are very reliable.
More Plastic Tubing Manufacturers
Plastic tubes are incredibly versatile, finding use in a wide range of applications, primarily for piping and hose purposes to transfer substances from one location to another. They play a crucial role across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, mechanical engineering, gas and oil, healthcare and medicine, agriculture, and water management.
In aerospace engineering, we use plastic tubing to transfer fuels, hydraulics, and other fluids. It serves similar purposes in automotive and mechanical devices. In the oil and gas industry, plastic tubing handles various fuels, including petroleum, natural gas, butane, and gasoline. In healthcare, it plays a crucial role in blood transfusions, intravenous drug delivery, catheterization, and other applications. For agriculture, plastic tubing facilitates the transfer of bulk solids and fluids on farms. Additionally, in water management, plastic tubing is indispensable for water treatment, irrigation, drainage, and plumbing.
Plastic tubing is crafted from polymers and select additives to achieve either flexibility or rigidity based on its intended use. It serves diverse applications, including fluid flow lines, insulation for heating and electrical systems, and construction materials. Available in numerous diameters, wall thicknesses, and strengths, plastic tubing is known for its durability and seamless construction, eliminating potential stress points.
They manufacture plastic tubing using either pultrusion or extrusion processes.
The History of Plastic Tubing
The history of plastic tubing traces back to the origins of piping itself. Before plastics existed, humans relied on various materials to create pipes. From the earliest days of plumbing, ancient civilizations such as the Chinese, Indians, Persians, Greeks, and Romans employed pipes—initially made of earthen materials and later lead—to transport drinking water and manage waste.
Centuries later, in the American West, wooden pipes became the preferred choice for water transport due to their easier maintenance compared to metal alternatives. By the 1800s, redwood trees were favored for their superior resistance to fungus, acids, insect damage, and weathering. In contrast, iron pipes quickly succumbed to corrosion and limescale buildup. During this period, they also began the transition towards the widespread use of plastic pipes.
In 1856, Alexander Parkes pioneered the creation of the first synthetic plastic, known as Parkesine. Crafted from cellulose treated with nitric acid and a solvent, Parkesine earned a bronze medal at the 1862 London World’s Fair. Parkes designed it as a substitute for ivory. As the 19th century progressed into the 20th, chemists rapidly developed a multitude of new plastic varieties, with a particularly intense period of innovation following both World Wars I and II. During these times, scientists worldwide focused on developing plastic materials to support the war effort. The post-war era of the 1940s and 1950s saw a dramatic surge in plastic usage, with plastic tubing increasingly replacing other materials. Notably, in 1945, plastic catheters were used for the first time as IVs in medical practice.
Nowadays, plastic tubing is primarily crafted from synthetic materials, though there’s a growing trend toward using tubing made from renewable resources. Raw plastic materials are widely available, often originating from hydrocarbon sources, which are typically derived from refined petroleum products. For instance, some types of raw plastics, like nylon 11, can be produced from castor oil, a renewable resource. Additionally, there are plastics made from non-hydrocarbon sources. Looking ahead, it’s anticipated that manufacturers will increasingly embrace more sustainable and eco-friendly options.
Plastic Tubing Design
Production
Raw plastic stock can be transformed into plastic tubing through various methods, including cell casting, plastic pultrusion, and plastic extrusion.
Cell Casting
Cell casting, one of the oldest techniques for fabricating plastic tubing, involves pouring molten plastic into a tube-shaped mold. Despite its long history, this method has several drawbacks: it is expensive, labor-intensive, time-consuming, and often inconsistent.
Plastic Pultrusion
Pultrusion is a technique that fuses plastic resins with fibers to produce a remarkably strong and durable material. This process is commonly employed in scenarios where tubing and equipment experience frequent or heavy impacts with other moving objects.
Plastic Extrusion
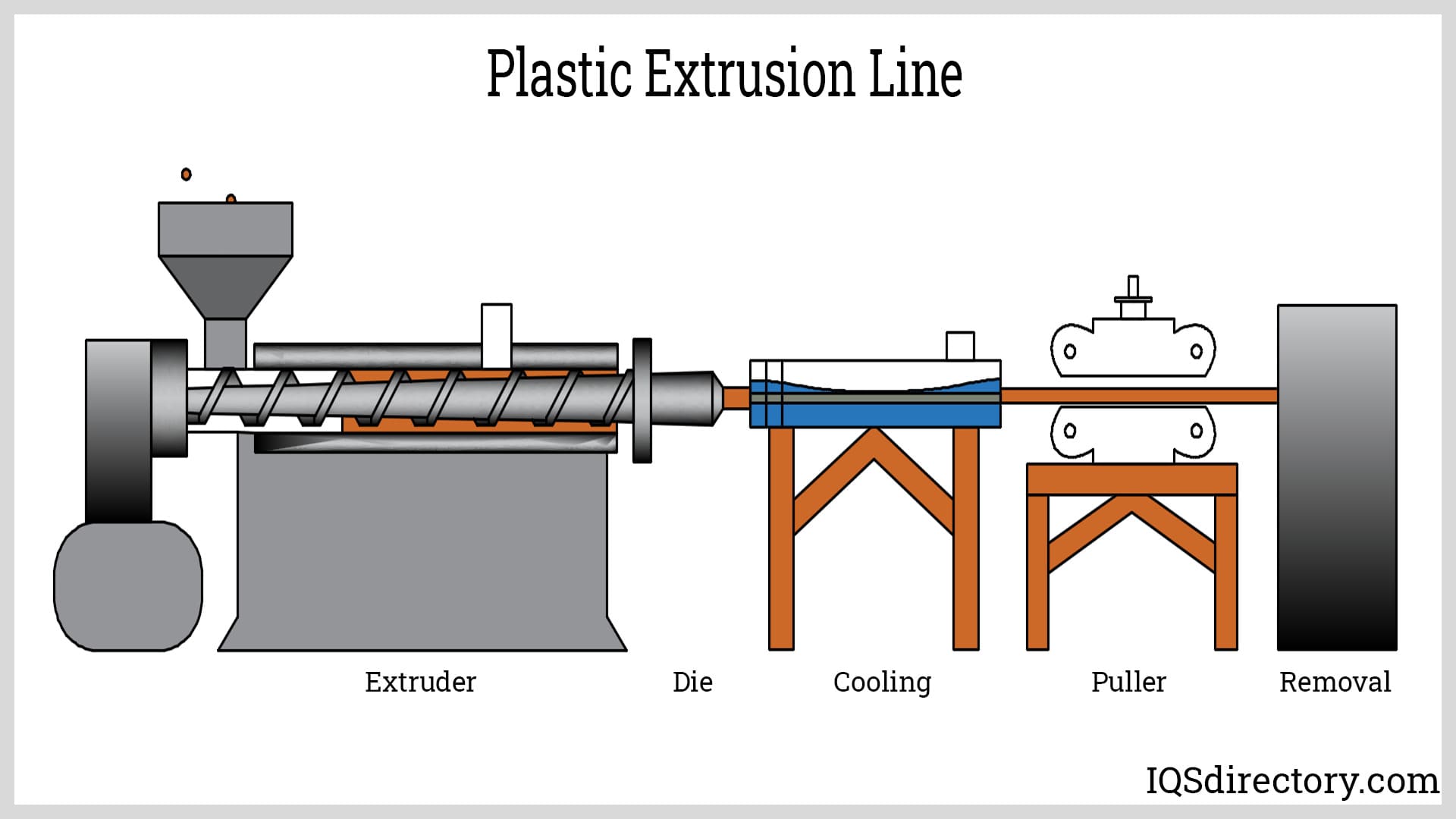
Pultrusion is a well-known technique, but plastic extrusion is far more widely used and stands out as the most efficient and effective method for fabricating plastic tubing. This process allows us to create tubes from any plastic material, accommodating a wide range of thicknesses and widths.
To extrude plastic, manufacturers of plastic tubing start by gathering raw plastic material. This material is then loaded into a hopper positioned above a conveyance channel. A long screw within the channel pushes the plastic forward, and as it moves, friction from the turning screw combined with heating elements integrated into the channel melts the plastic into a liquid state.
At the end of the channel, a die—a tool used to shape raw material into a product—plays a crucial role. This die is a metal plate featuring a precisely designed hole. As molten stock is pushed through this hole, it emerges as a freshly extruded plastic tube. From here, the tube can be cut to length, readied for shipping, or sent for further processing.
Materials
They commonly use a range of materials, including flexible vinyl, polyurethane, low and high-density polyethylene, cross-linked polyethylene, rigid vinyl, polycarbonate, polystyrene, PETG, and various nylon types. Each of these materials has unique qualities that distinguish them from one another.
- Polyurethane boasts exceptional resilience and resistance to chemicals and abrasion. It endures high pressures and strong impacts with ease. Polyurethane tubing is particularly adept at handling hydrocarbons, gasoline, and other petroleum-based chemicals.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a versatile material known for its flexibility and strength, offering excellent resistance to chemicals and wear. Its hygienic and non-toxic properties make it ideal for transporting fluids in industries like food and beverage manufacturing and medical fields. For enhanced corrosion resistance at elevated temperatures, PVC resins can be chlorinated to create chlorinated PVC. To increase flexibility, plasticizers can be added to PVC tubes.
- Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) exhibits resistance to corrosive liquids and gas and is chemically inert; hence it is used in chemical manufacturing and laboratories. It can endure very low or high temperatures without cracking. It effectively transports liquids because its surface has a low coefficient of friction.
- Polycarbonate is a durable material known for its high strength, impact resistance, and flame resistance. It performs reliably across a broad range of temperatures and can be machined and drilled without risk of cracking. However, it is prone to scratching and requires a hard outer coating to protect its surface.
- Fiberglass plastic blends fiberglass with thermosetting plastic, creating a material that is both tough and lightweight. It maintains its shape and strength over time while offering exceptional resistance to corrosion, UV light, and flames. Additionally, it withstands aggressive chemicals and provides excellent electrical insulation.
Customization
Manufacturers tailor plastic tubing to meet specific application requirements, such as flexibility, strength, stretch, color, sterility, corrosion resistance, load capacity, and cost. They also consider factors like the frequency of access or maintenance and the substances the tubing will handle, including hazardous materials. These considerations influence decisions on tubing material, wall thickness, diameters, fittings, length, and coatings. Additionally, not all applications are suited to cylindrical tubing, so some fabricators also produce square and other specialized tubing shapes.
Features of Plastic Tubing
Plastic tubing is straightforward to use. It’s designed to seamlessly integrate with your application components, which usually consist of fittings, flow meters, and the fluid intended to flow through it. In some instances, the tubing relies on gravity to guide fluids along the path of least resistance, as seen in many drainage applications.
Types of Plastic Tubing
Acrylic Tubing
Acrylic tubing, often referred to as clear plastic tubing, can be manufactured in both opaque and nearly transparent forms. Naturally clear acrylic sheet tubes are commonly used in applications where it’s essential to observe the contents flowing through the tubes. Clear acrylic and clear plastic tubing play a crucial role in the medical industry. Additionally, acrylic tubes can be tinted, which facilitates the organization of tubes that are placed close together.
Poly Tubing
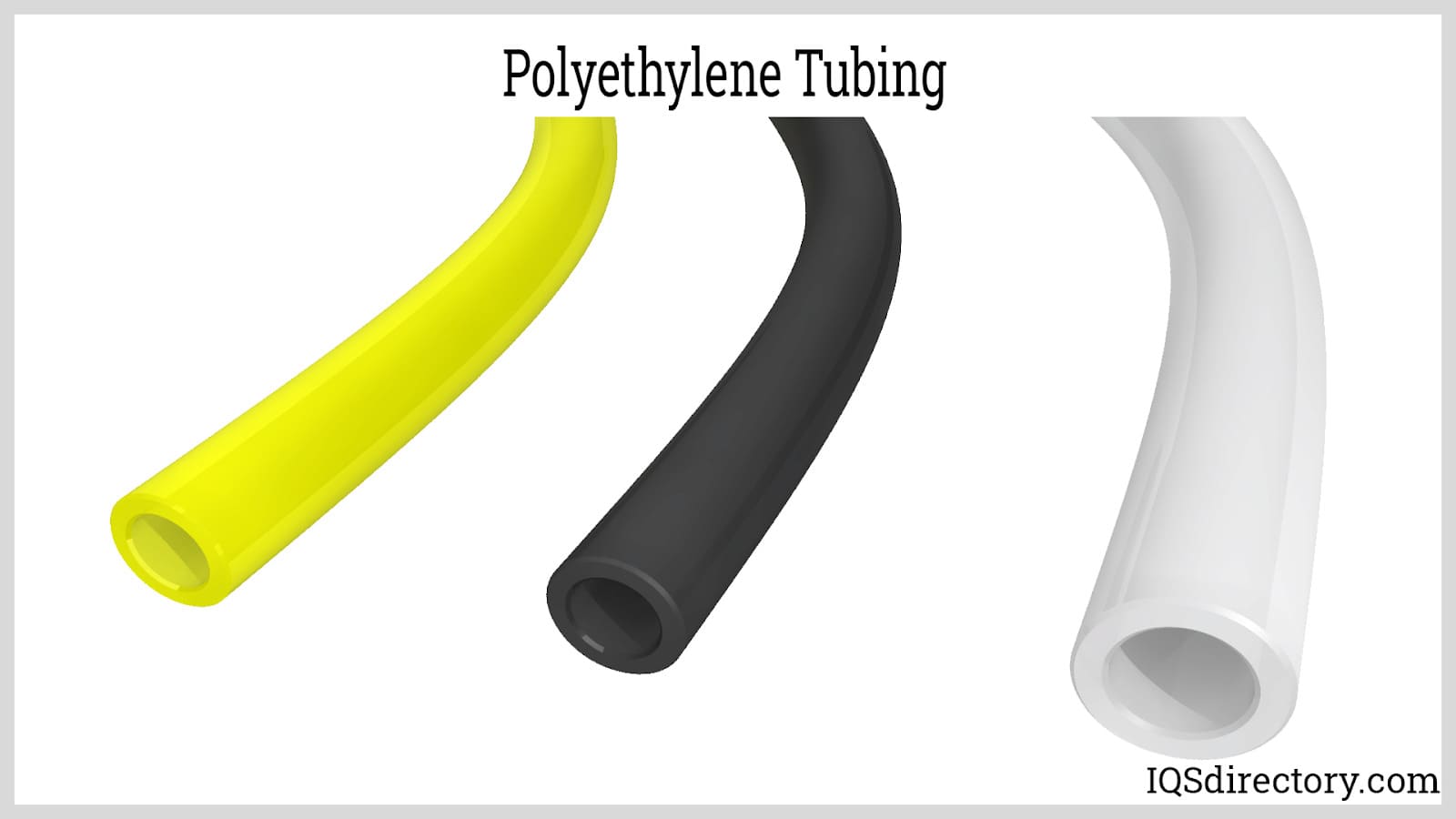
For those seeking a more durable material, polyethylene tubing, also known as poly tubing, is an excellent choice. High-density polyethylene tubes, often abbreviated as HDPE plastic tubes, are perfect for high-impact applications. Conversely, low-density polyethylene tubes, or LDPE tubes, offer greater flexibility and are commonly used in pneumatic equipment.
Low-density polyethylene produces flexible plastic tubing, whereas high-density polyethylene is used to create tubing that is stronger, more rigid, and more impact-resistant.
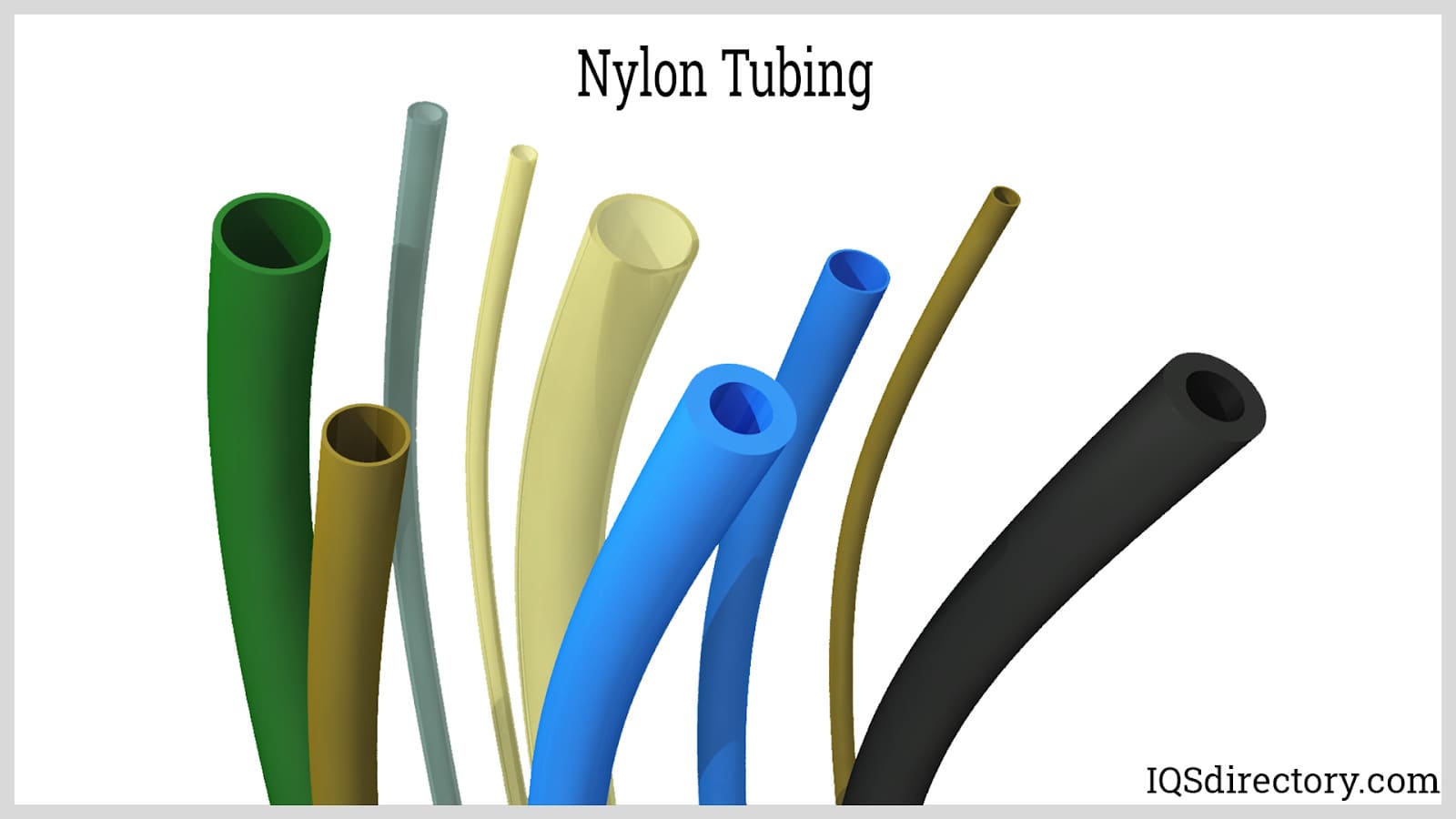
Nylon Tubing
Nylon tubing, a popular choice for pneumatic applications, can be made from non-petroleum-based raw materials in some varieties. It offers excellent heat and crack resistance, making it suitable for automotive fuel lines, refrigerator water lines, and a range of other uses. Its versatility extends across various industries, including aerospace, filtration, medical technology, irrigation, and laboratory settings, among others.
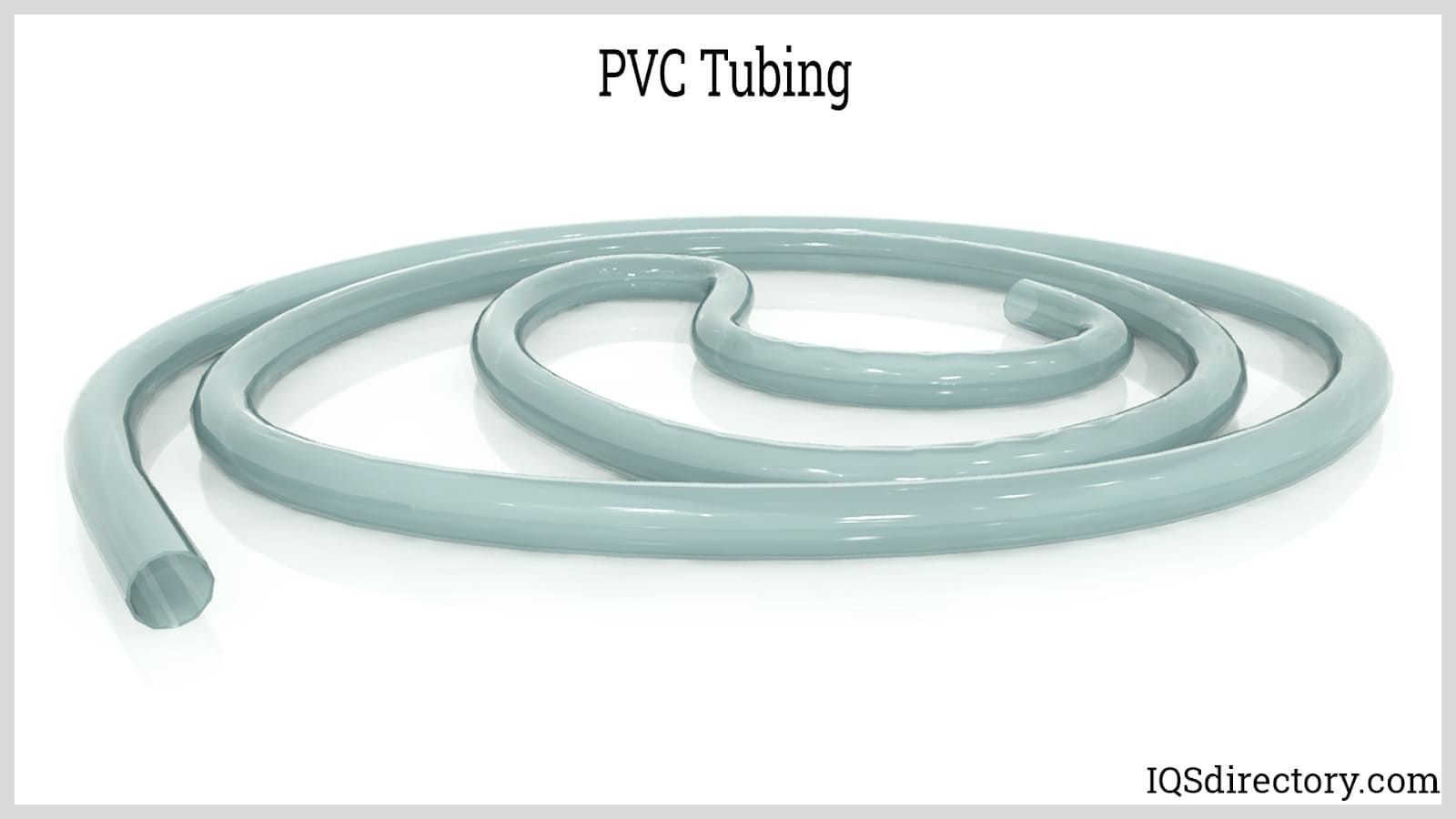
Vinyl Tubing/PVC Tubing
Vinyl tubing, made from plastics in the vinyl chemical group, primarily consists of polyvinyl chloride (PVC). PVC tubing stands out as one of the most versatile materials in the plastic world. It finds extensive use across various industries, including consumer goods, construction, industrial settings, heating and cooling systems, and plumbing. PVC’s key advantages include its resistance to corrosion, non-conductive nature, nontoxicity, durability across extreme temperatures and pressures, and ability to handle high flow volumes. These attributes make PVC tubing an excellent choice for applications such as food processing, brewing, pool maintenance, and industrial wastewater management.
Heat Shrinkable Tubing
Heat shrinkable tubing is a specialized material engineered to shrink when exposed to heat. It is crafted to create a snug, glove-like insulative cover.
Corrugated Tubing
Corrugated tubing is characterized by its distinct pattern of tight ridges and perpendicular valleys running the length of the tube. This design provides exceptional sturdiness while maintaining a low flow rate. Typically crafted from low-density linear plastics such as polyethylene, PVC, polyurethane, or nylon, it can be designed for either reusable or disposable applications. Corrugated tubing comes in a wide range of sizes, with 10 mm being a common standard. It is predominantly used in medical settings for applications such as administering anesthesia and supporting respiratory ventilators.
Medical Tubing
“Medical tubing” encompasses any plastic tubing utilized in medical procedures or applications, including catheters, IV drips, and surgical use.
Plastic Pipe
“Plastic pipe” generally describes highly rigid and inflexible plastic tubing. It is usually measured by its inner diameter.
Hard Plastic Tube
Hard plastic tubing offers a slightly lower rigidity compared to plastic pipe. This tubing, which is less rigid and flexible, is selected for its resistance to abrasion and kinks, as well as its overall strength. Available in both clear and opaque options, hard plastic tubing is commonly made from acrylic or polycarbonate.
Advantages of Plastic Tubing
Plastic tubing stands out as an exceptional choice for numerous reasons. Its versatility is unmatched, thanks to the wide range of plastic materials available. This diversity allows manufacturers to select a material that meets virtually any application need, whether it involves extreme temperatures, high pressures, or significant corrosion resistance. Additionally, plastic tubing is cost-effective to produce. With the right expertise, it offers both efficiency and effectiveness for your specific requirements.
Plastic Tubing Accessories
Based on your application requirements and specifications, you might require various accessories, such as fittings, connectors, joints, valves, inserts, or couplings.
Proper Care for Plastic Tubing
Taking good care of your plastic tubing ensures its longevity. Start by regularly inspecting its condition for issues such as leaks, cracks, corrosion, and tears. While some plastic tubing is designed to fail safely in case of a leak, others are not. Tubing that falls into the latter category can present a higher risk of explosion or shattering if compromised.
If you discover that your plastic tubing is compromised, address the issue quickly. In some cases, you can repair a pinhole leak by cutting out the damaged section and reconnecting it with a coupler. However, if the damage is extensive, replacement may be necessary. Given the wide range of plastic tubing characteristics, consult your manufacturer for specific care instructions.
Plastic Tubing Standards
The standards for your plastic tubing are influenced by its application, industry, and region. For instance, drinking straws and surgical tubing must meet FDA regulations, while plastic pipes must comply with EPA standards, which are guided by ASTM. If you intend to use non-pressure plastic pipes or tubing on American roadways, they must adhere to the EPA standards set by the AASHTO (American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials). To ensure your plastic tubing meets all requirements, consult with your manufacturer, industry leaders, or the relevant government offices before moving forward.
How to Find the Right Plastic Tubing Manufacturer
Plastic tubing is a common product with countless companies offering fabrication services. Sorting through them to find the right one can feel overwhelming. Luckily, we’ve already done much of the legwork for you. We’ve curated a list of manufacturers we trust and believe in. Simply scroll up a bit to discover profiles of several highly skilled and reliable manufacturing companies.
We’ve given you a selection of companies to explore. To make your choice, start by reviewing their profiles and websites to identify those that seem to meet your needs. Select a few—about three or four—that you’d like to contact directly. Reach out to each of them to discuss important factors like custom plastic tubing services, secondary services, lead times, delivery options, standard certifications, and budget. Be sure to check customer reviews and seek out strong references. Ensure that the company you choose aligns with your best interests. After your discussions, compare the options and choose the one that best fits your needs. Then, give them a call and start the process.







 Fiberglass Fabricators
Fiberglass Fabricators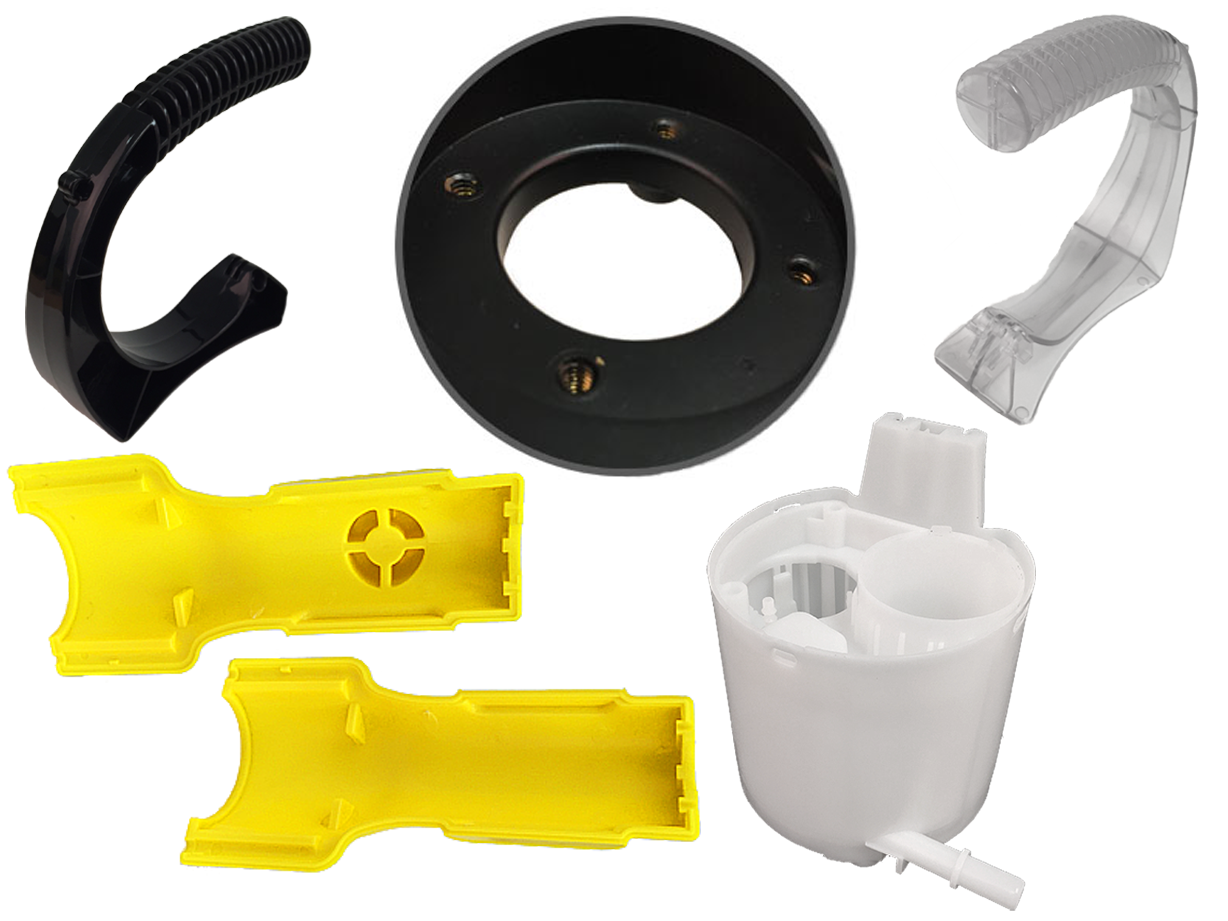 Injection Molded Plastics
Injection Molded Plastics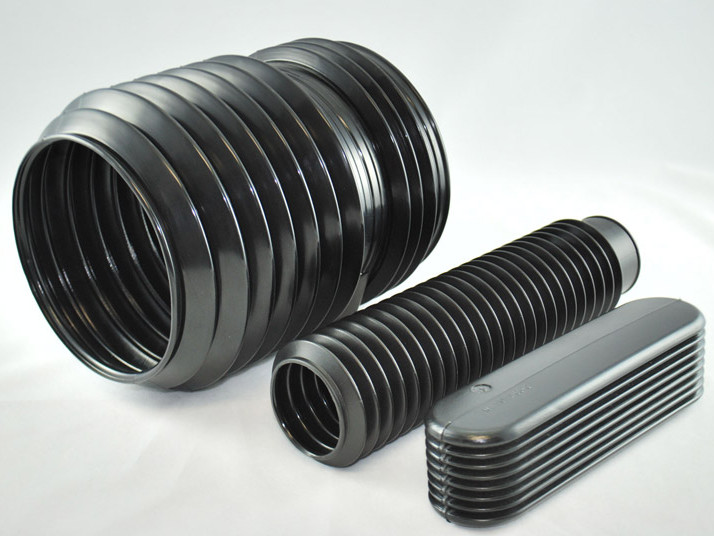 Plastic Blow Molding
Plastic Blow Molding Plastic Dip Molding
Plastic Dip Molding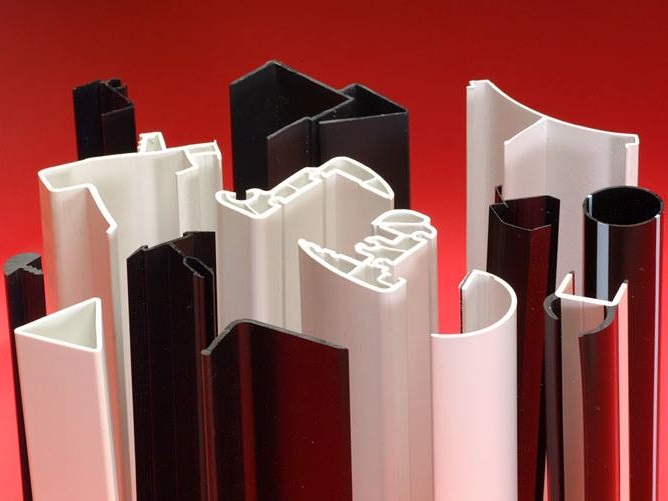 Plastic Extrusions
Plastic Extrusions Plastic Tubing
Plastic Tubing Polyurethane Molding
Polyurethane Molding Rotational Molding
Rotational Molding Vacuum Forming
Vacuum Forming Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services